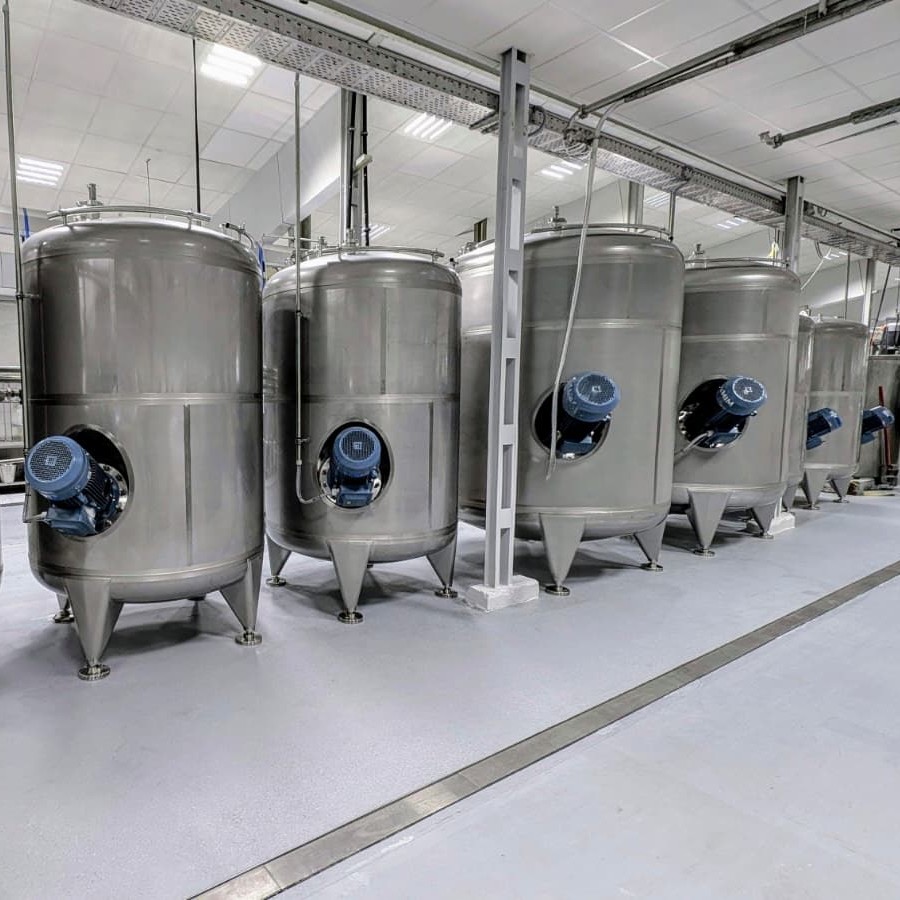
Used stainless steel tanks as heat storage: efficiency and sustainability for industry and energy plants
In industrial processes and biomass power plants, excess heat often accumulates and frequently goes unused. Used stainless steel tanks offer an efficient solution: as buffer tanks, heat storage tanks, or stratified storage tanks, they can temporarily store heat and release it as needed. This saves energy, reduces CO₂ emissions, and lowers costs.

Heat Storage with System: Buffer Tanks in Industrial Use
Whether in the food and chemical industry or in the pharmaceutical and energy sectors – buffer tanks compensate for fluctuations between heat supply and demand.
Example: A large dairy uses waste heat from production, stores it in a 300,000-liter stainless steel tank, and feeds the heat into two networks. Result: 15% higher energy efficiency and noticeable savings on electricity and fuel.
Why Used Stainless Steel Tanks?
- High quality and durable: Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant, hygienic, and temperature-resistant.
- Cost-efficient: Used tanks are often immediately available and significantly cheaper than new products.
- Sustainable: Reuse saves up to 5 tons of CO₂ per tank – through saved materials and manufacturing effort.
Many suppliers professionally refurbish used tanks: cleaning, pressure testing, fittings, and insulation included. This creates economical heat storage solutions for projects starting from about 10,000 liters in volume – ideal for medium to large applications.
Pressurized and Non-Pressurized Solutions
Depending on temperature and system requirements, heat storage tanks are designed as pressurized (closed) or non-pressurized (atmospheric) vessels.
- Pressurized tanks: Suitable for temperatures above 100 °C and closed heating systems.
- Non-pressurized storage: Ideal for lower temperatures, e.g. in district heating or solar thermal systems.
Stainless steel stands out for its durability – even with oxygen ingress.
Stratified Storage: Distributing Heat Efficiently
Through temperature stratification, a storage tank can simultaneously provide heat at different levels. In biomass power plants, this enables efficient load management: hot water is available at the top for peak demands, cooler water is reheated at the bottom.
Stainless steel tanks in a vertical design are particularly suitable for this type of heat distribution.
Practical Application Examples
- Dairies & Breweries: Process heat from pasteurization or cleaning is buffered and reused.
- Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals: Discontinuously generated heat can be stored and used in subsequent process steps.
- Biomass Power Plants: A 200,000-liter storage unit in Kelheim saves around 62 tons of CO₂ annually and enables demand-driven heat usage.
Modular storage solutions with multiple tanks (e.g. 3 × 50,000 liters) are also possible – for example, when space is limited or heat is generated in stages.
Advantages at a Glance
- Energy efficiency through heat recovery
- Cost advantages through reuse & lower investment costs
- Climate protection through CO₂ savings & circular economy
- Flexibility in size, pressure level, and equipment
Conclusion
Used stainless steel tanks are more than just a cost-effective alternative – they are a key element for sustainable, economical, and future-proof energy systems. From medium-sized food producers to municipal energy providers: the reuse of high-quality tanks as heat storage units is worthwhile.
Sie möchten mehr zu dieser Leistung erfahren?
Sprechen Sie uns an.